本文最后更新于:2023年11月9日 晚上
Swagger-概述
Swagger 是一款RESTFUL接口的文档在线自动生成+功能测试功能软件。
Swagger 是一个规范和完整的框架,用于生成、描述、调用和可视化 RESTful 风格的 Web 服务。总体目标是使客户端和文件系统作为服务器以同样的速度来更新。文件的方法,参数和模型紧密集成到服务器端的代码,允许API来始终保持同步。Swagger让部署管理和使用功能强大的API从未如此简单。
本篇将使用SpringBoot进行搭建Swagger
1. maven导入Swagger包
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| <dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.springfox</groupId>
<artifactId>springfox-swagger2</artifactId>
<version>2.9.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.springfox</groupId>
<artifactId>springfox-swagger-ui</artifactId>
<version>2.9.2</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
|
2. 配置开启swagger2
新建一个配置类,然后开启使用@EnableSwagger2注解就可以了
注:在后续的操作中都是在swagger配置类中进行
1
2
3
4
5
| @Configuration
@EnableSwagger2
public class swaggerConfig {
}
|
3. 测试swagger
在此之前可以编写一个测试的Controller,效果更佳显著
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| @Controller
public class swaggerController {
@RequestMapping(path = "/hello")
@ResponseBody
public String hello(){
return "hello swagger";
}
}
|
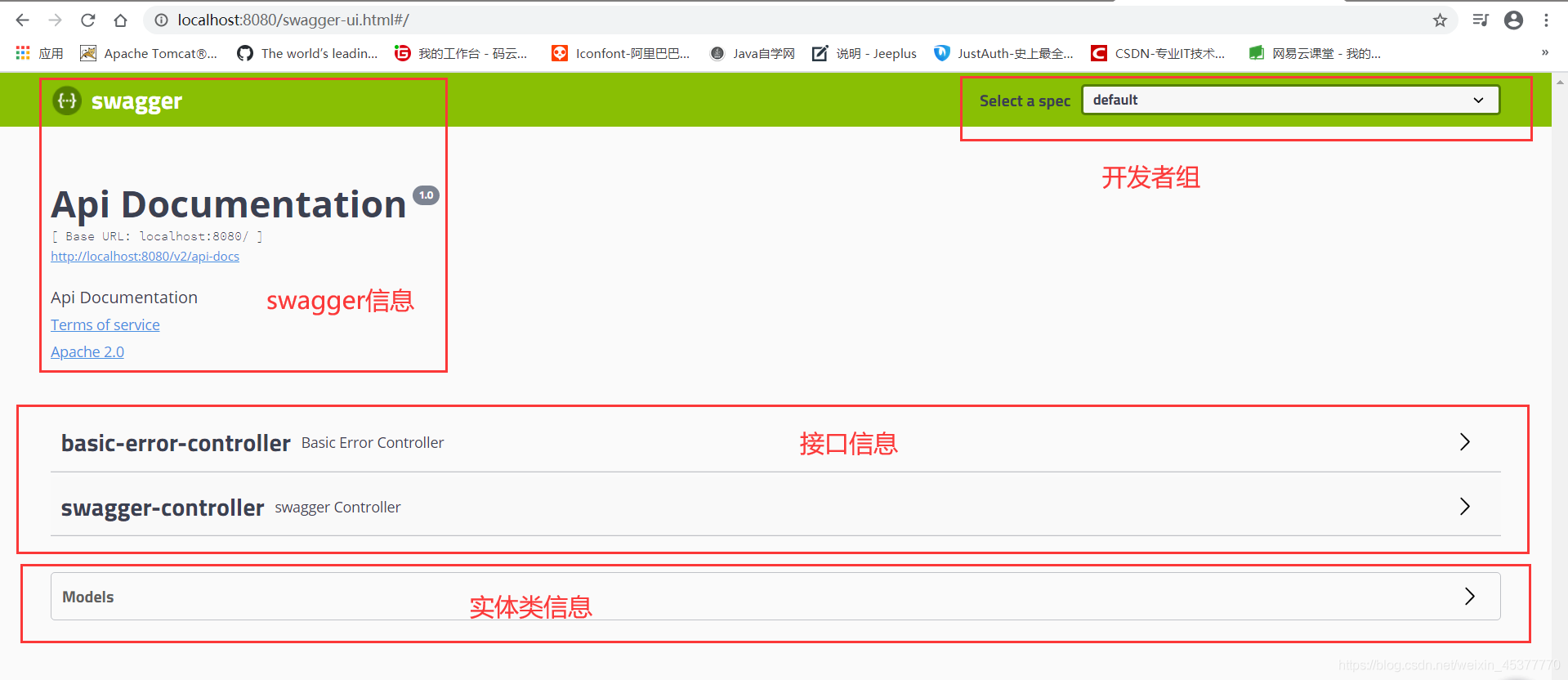
启动项目进行访问swagger:http://localhost:8080/swagger-ui.html
能够看到此页面代表swagger基础配置就完成了,swagger页面分为4个内容
- swagger信息:相当于作者的个人信息(可自行修改)
- 接口信息:在controller中编写的接口全在里面(SpringBoot默认有个接口就是error)
- 实体类信息:对应数据库表中的数据字段
- 开发者组:是一个下拉框,可以创建不同的开发者信息(比如某些业务的接口是01开发的,某些接口是02开发的)
4. 配置swagger信息
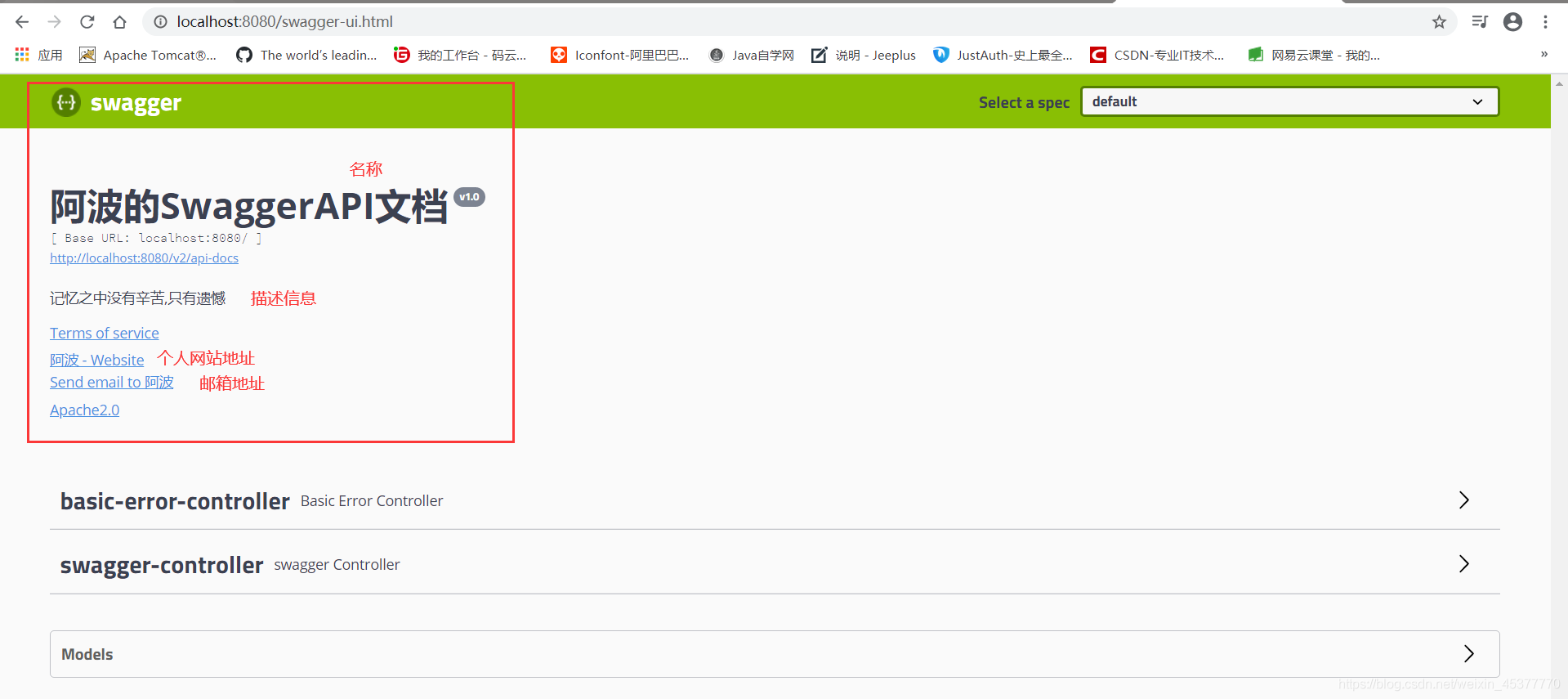
swagger信息:开发者名称、个人网站地址、邮箱地址、描述信息…(可以根据不同的Docket获取不同的ApiInfo中Contact的name属性来区别接口的开发者)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
| @Configuration
@EnableSwagger2
public class swaggerConfig {
@Bean
public Docket getDocket( ){
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2).apiInfo(apiInfo());
}
private ApiInfo apiInfo( ) {
Contact contact = new Contact("阿波","https://libo2000.github.io/","973747397@qq.com");
return new ApiInfo(
"阿波的SwaggerAPI文档",
"记忆之中没有辛苦,只有遗憾",
"v1.0",
"https://libo2000.github.io/",
contact,
"Apache2.0",
"https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0",
new ArrayList<>()
);
}
}
|
修改完之后再次访问:http://localhost:8080/swagger-ui.html 明显的看到swagger信息与之前发生了变化
5. 配置swagger扫描接口
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
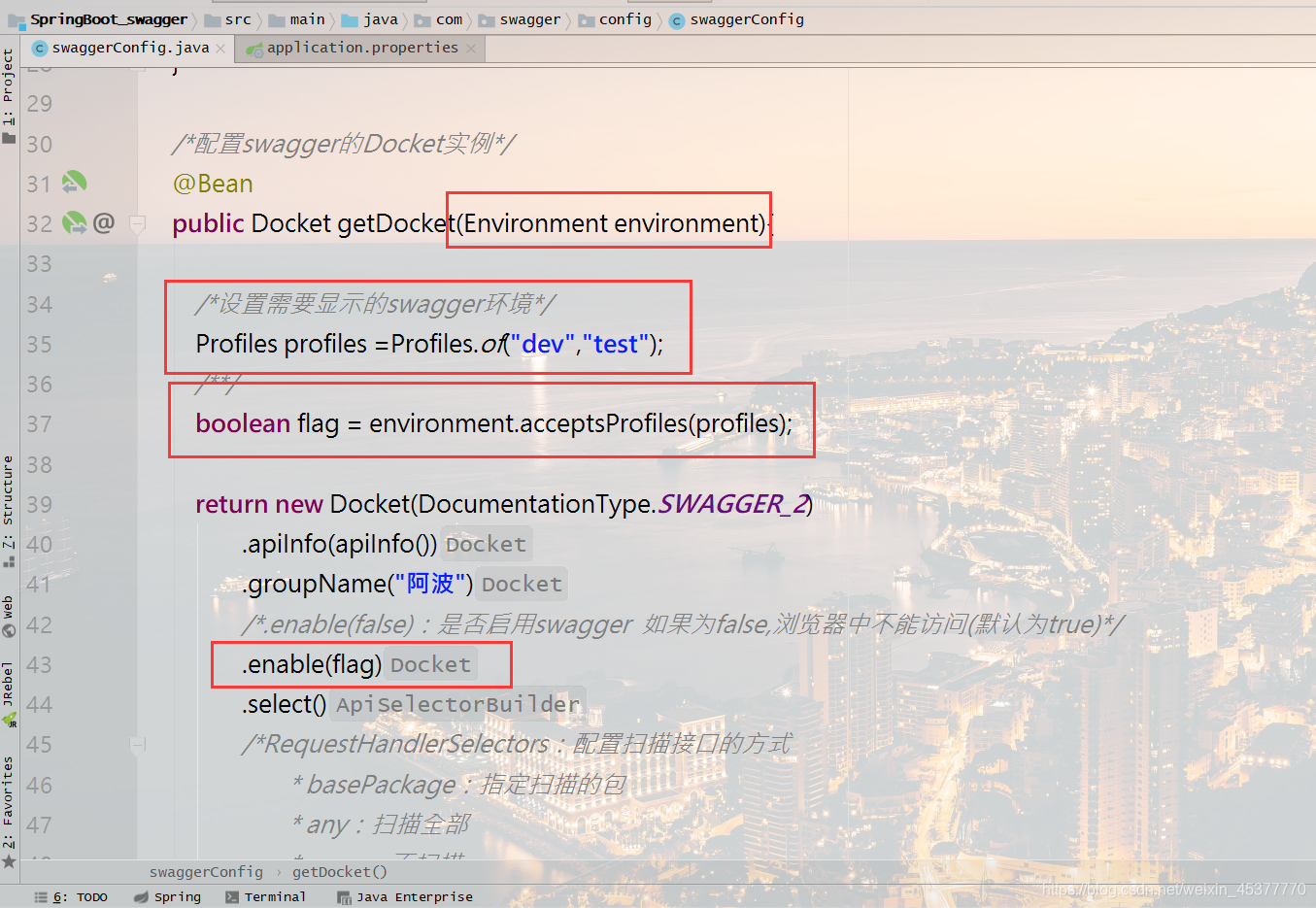
@Bean
public Docket getDocket(Environment environment){
Profiles profiles =Profiles.of("dev","test");
.enable(flag)
.select()
.apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage("com.swagger.controller"))
.build();
}
|
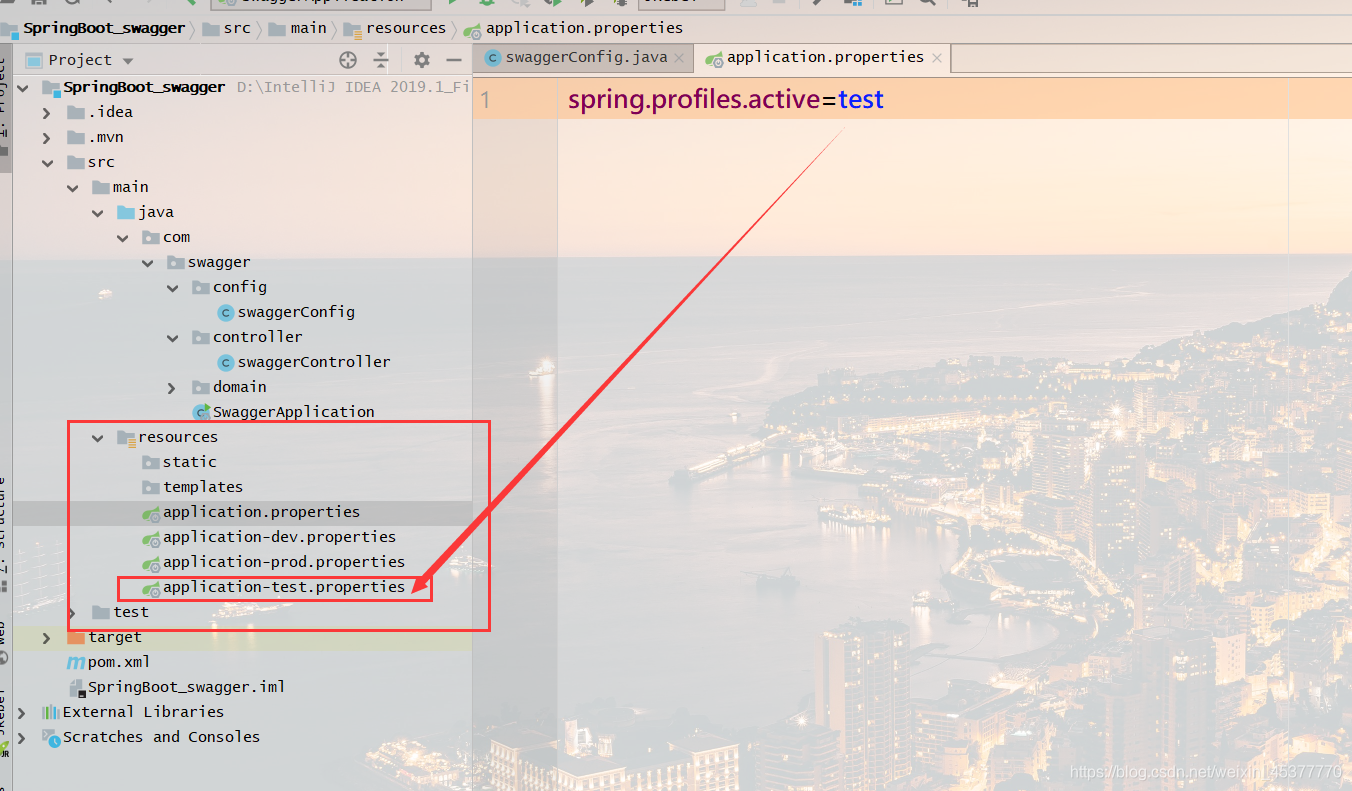
这里有个问题:这么才能控制swagger的显示问题,Docket实例中enable()默认为true就是说可以访问(false则不能访问),但是我想让swagger在测试阶段才可以访问,其他时候不能访问,如何实现?
方便我们测试所以创建多个SpringBoot的配置文件properties,在主配置文件中配置spring.profiles.active=具体配置环境(代表当前项目使用的是那一个项目环境)
- 设置需要显示的swagger环境(例如:只有在dev或者test环境下才显示):Profiles profiles =Profiles.of(“dev”,”test”);
- 判断当前环境是否为设置的环境(返回boolean值true或false):boolean flag = environment.acceptsProfiles(profiles);
- 将flag变量传到Docket实例的.enable(flag)属性中:enable(flag)
至此就可以通过获取当前环境而控制swagger的访问
6. swagger分组与接口注释
swagger分组:
在swagger配置时可分为不同的多个Docket对象,相当于每一个Docket对象就是一个项目中的开发者。可以设置多个ApiInfo信息,再通过Docket的groupName()参数为ApiInfo中Contact对象的name成员变量,在上面我们知道了Docket中可以设置扫描接口,那我们在通过扫描不同的接口、配置不同的ApiInfo信息,那么就可以进行swagger的分组(就可以在swagger中区别不同开发者写的接口及代码)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
| @Configuration
@EnableSwagger2
public class swaggerConfig {
@Bean
public Docket getDocket2(){
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2).groupName("阿波2");
}
@Bean
public Docket getDocket3(){
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2).groupName("阿波3");
}
@Bean
public Docket getDocket(Environment environment){
Profiles profiles =Profiles.of("dev","test");
.enable(flag)
.select()
.apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage("com.swagger.controller"))
.build();
}
private ApiInfo apiInfo() {
Contact contact = new Contact("阿波","https://libo2000.github.io/","973747397@qq.com");
return new ApiInfo(
"阿波的SwaggerAPI文档",
"记忆之中没有辛苦,只有遗憾",
"v1.0",
"https://libo2000.github.io/",
contact,
"Apache2.0",
"https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0",
new ArrayList<>()
);
}
}
|
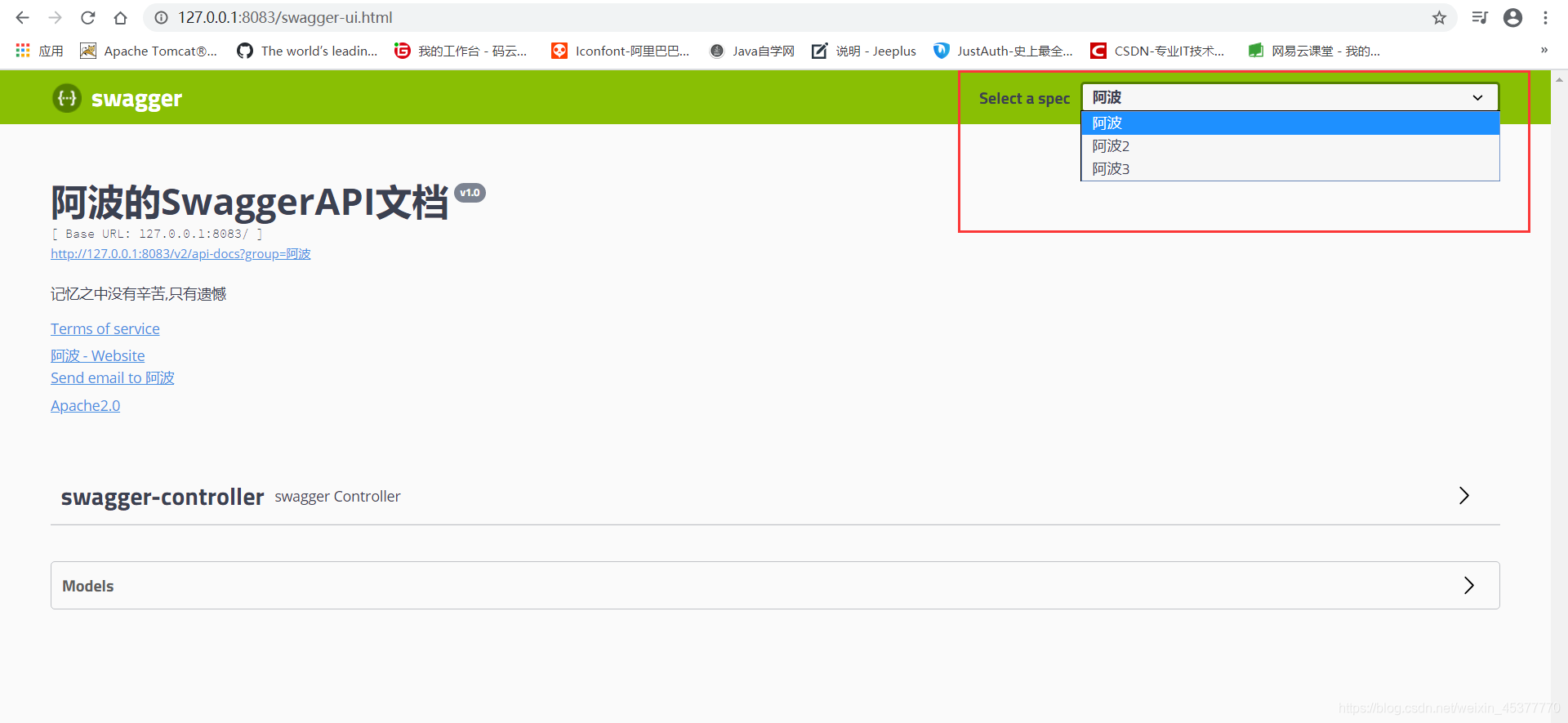
swagger常用注解
在swagger如何去描述实体类呢?(JavaBean)
首先创建实体类,然后对实体类及成员变量通过注解进行描述:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| @ApiModel("用户实体类")
public class User {
@ApiModelProperty("用户名")
public String username;
@ApiModelProperty("密码")
public String password;
}
|
然后在Controller中进行接口配置:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| @RestController
public class swaggerController {
@GetMapping(path = "/hello")
public String hello(){
return "hello swagger";
}
@PostMapping(path = "/user")
public User user(){
return new User();
}
}
|
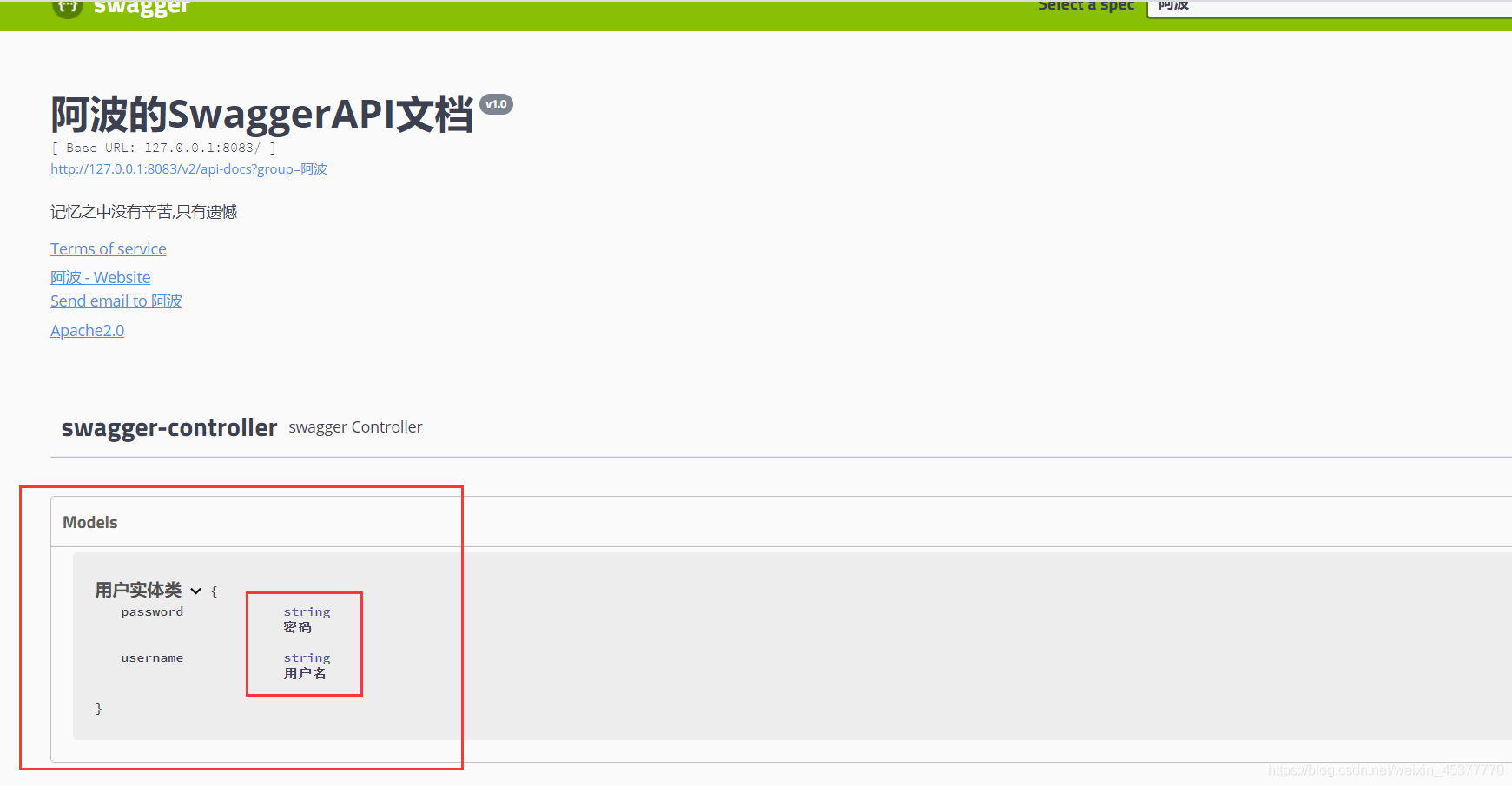
对接口的描述:
1
2
3
4
5
| @ApiOperation("user控制类")
@GetMapping(path = "/hello2")
public String hello2(@ApiParam("用户名") String username, @ApiParam("密码")String password){
return username+password;
}
|
Swagger常用注解
在Java类中添加Swagger的注解即可生成Swagger接口,常用Swagger注解如下:
- @Api:修饰整个类,描述Controller的作用
- @ApiOperation:描述一个类的一个方法,或者说一个接口
- @ApiParam:单个参数描述
- @ApiModel:用对象来接收参数
- @ApiModelProperty:用对象接收参数时,描述对象的一个字段
- @ApiResponse:HTTP响应其中1个描述
- @ApiResponses:HTTP响应整体描述
- @ApiIgnore:使用该注解忽略这个API
- @ApiError:发生错误返回的信息
- @ApiImplicitParam:一个请求参数
- @ApiImplicitParams:多个请求参数
现在的我,未来的我,一起去啊,更远的地方!






